Laser direct exposure with AR-P 3540
In addition to a structuring with photomasks which is frequently used in lithography, is it also possible to write the structures directly, i.e. without masks, with laser beams. The most commonly used wavelength for this purpose is the 405 nm line.
By merging classical mask-based exposure methods (contact, proximity and projection exposure) with modern maskless lithography (laser and electron beam exposure), mix & match technologies are possible which combine the high throughput of mask technology with a high resolution in the sub-µm range (laser).
This technology is in particular aimed at increasing the user’s efficiency of exposure techniques, in particular for MEMS and sensor technology processes.
In analogy to well-known photolithographic structuring procedures (see Resist-Wiki General Basic Chemistry), AR-P 3540 is chemically modified using a controlled laser beam and dissolved in the subsequent development. In test series, new fields of application for AR-P 3540 in maskless lithography were investigated and evaluated.
Good results are presented in the following figures – resolutions of significantly less than 1.0 µm were achieved.
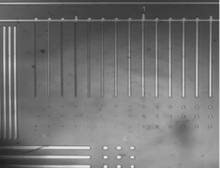
Fig. 1 Resolved structures (bars) <1.0 µm in AR-P 3540
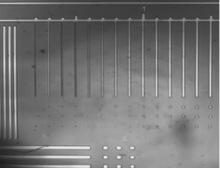
Fig. 2 Resolved structures (holes) <1.0 µm in AR-P 3540
According to information provided by Klaus-Dieter Preuß – development engineer at the CiS Research Institute for Micro Sensors and Photovoltaics GmbH and Dr. Axel Weidner – managing director of the ML Microlithography Service GmbH Jena (see also AR NEWS 28. issue)
Overview of photoresist-others
Adaptable two-layer resist AR-BR 5460 for variable lift-off structures
Alkali-stable, easily structurable positive resist SX AR-P 5900/8
Laser direct exposure with AR-P 3540
New procedure for the spray coating of deep topologies with SX AR-P 1250/20
Photoresist coatings on Teflon substrates
Positive resist for temperature sensitive substrates
Positive two- layer lift-off system
Resist for 488 nm exposure wavelength
Spray resists for different topologies (positive and negative)