Thermostable photoresists
Many applications demand coatings with excellent thermal stability. Structures of the temperature-stable negative resist SX AR-N 4340/6 are able to withstand temperatures of up to 350 °C with high shape accuracy (Fig. 1); merely shrinkage of up to 20% is observed (Fig. 2).
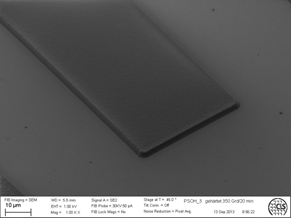
Fig. 1 REM-image of SX AR-N 4340/6 structure tempered at 350 °C with smooth surface and sharp edges
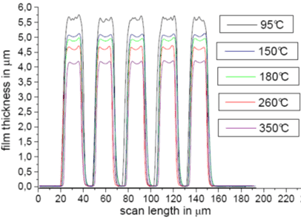
Fig. 2 Temperature-dependent shrinkage, measured with Dektak 150
Structures of the new thermostable positive resists SX AR-P 3500/8 also show a great resistance to very high temperatures as they occur for example in intensive etching or implantation processes. Most commercially available removers easily dissolve resist layers after thermal loads of up to 130 ° C. At higher temperatures however, the aqueous alkaline remover AR 300-73 has to be used. Hardened structures (above 150 ° C) are then inert to solvents, which enables applications in microfluidics.
Overview of photoresist-others
Alkali-stable positive resist obtained after treatment with HMDS
Aqueous negative resist based on gelatine
Atlas 46 for nanoimprint lithography
Ethanol and toluene-resistant photoresist AR-U 4060
Fluorescent resist structures with photoresists
Laser ablation of PPA (Phoenix 81)
Negative CAR PMMA resist SX AR-N 4810/1
Positive polyimide one-layer resist
Resist for near infrared (NIR)
Structuring by ablation of the resist materials
Structuring of polyphthalaldehydes with photolithography
Surface imaging resist system SX AR-N 7100 – silylable photoresist
Thermostable photoresists
Top surface imaging (TSI) photoresist – principles
Two-layer photoresist system for water-sensitive substrates
Two-layer resist system for hydrofluoric acid etching