Dose-dependent structure size with negative resists
The desired structure size also largely depends on the exposure dose used. In the case of overexposure, structures begin to widen which is particularly pronounced during laser exposure. The image series shows 5 µm-columns obtained with different doses. The determined minimum dose is not high enough for a complete build-up of the 5 µm-column, which results in a pointed cone. With increasing doses (30 mJ/cm² and above), the shape of a column is obtained. At higher values (70 mJ/cm² and more), the diameter of the cylinder increases due to the overexposure and the scattered light associated with it. At 120 mJ/cm², already a diameter of 7.5 µm is reached. Overexposure similarly results in larger structures if mask aligners are used for exposure (photolithography). It is thus strongly recommended to determine the optimum dose at the beginning of the application.
Image series 6 with different doses:
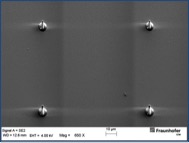
7 mJ/cm² 5 µm
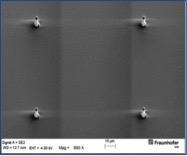
40 mJ/cm² 5 µm
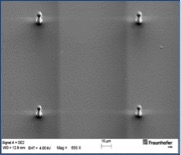
70 mJ/cm² 5 µm
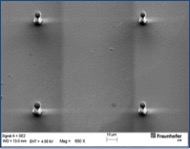
90 mJ/cm² 5 µm

120 mJ/cm² 5 µm
Overview of negative photoresist
Alkali-stable and solvent-stable negative resist
Chemically enhanced negative resist (Process parameters and resolution)
Chemically enhanced negative resist without cross-linking
Coloured negative photoresists
Development of thick negative resist layer
Dose-dependent structure size with negative resists
Fabrication of vertical flanks with CAR 44
Generation of undercut structures with negative resists
Negative polyimide photoresist
Negative two- layer lift-off system
NIR-laser structurable photoresists
poly(hydroxystyrene) and (hydroxystyrene-co-MMA) photoresist with high-temperature stability
Sensitive negative PMMA resist (CAR)
Sensitive negative resist for 405 nm laser direct exposure